As a student developer at EdPlus at Arizona State University, I had the opportunity to work on project that involved to display analytic information of the ASU website. A colleague prior to me was involved in building the entire application. He decided to use a web application MVC framework Express - Node.js. We'll its a good choice easy to manage as each of the component is pretty decoupled, the model view and the controllers as known as routes in NodeJS. The entire project was deployed on a HTTP server on Amazon. The project was basically displaying google analytic data. There was no session database etc. Just a simple application that uses data from google analytics and displays content using various charts.
I was given the opportunity to work on it take it further. I was hard stuck that MVC is the best existing model to decouple your project and have easier code management.
Perhaps this discussion changed it all:
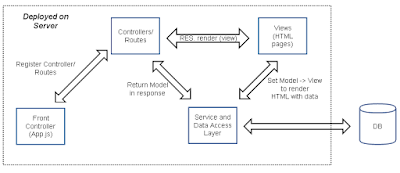
There are quite a number of MVC frameworks out there. Some of them back of mind would be spring MVC in Java, Express in Node.js. When a request arrives to the server it first lands on the front controller as shown in the figure above. In spring MVC its the dispatcher servlet or Node.js its app.js/server.js (the file that declare itself as a server application. There a various controllers/routes registered on to the front controller. Based on the URL path the front controller dispatches the request to the entity specific controller.
So lets take an example https://www.domain.com/app_name/entity_path/entity_api_method
Now as soon as the request arrives to Front Controller it checks for the entity_path registered with it and forwards the request to the entity specific controller. Then in that controller it scans for the API that matches 'entity_api_method' and renders the specific view or returns model for service/data access layer or any 3rd party API can be consumed here. All of this is deployed on a server.
My application did not have a database, no session management, no user access etc. Why do I need a server? Well I only realized when I read that blog by Tim Wagner.
Amazon provides EC2 or Elastic bean stalk (an environment to configure n instances of EC2) that can help you deploy your web application. However these configurations still host a server or is a server. But we decided a server-less architecture.
Here, AWS Lamda comes to the rescue!
Q: What is AWS Lambda?
"AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay only for the compute time you consume - there is no charge when your code is not running. With Lambda, you can run code for virtually any type of application or backend service - all with zero administration. Just upload your code and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability. You can set up your code to automatically trigger from other AWS services or call it directly from any web or mobile app " - AWS faq.
Lets start breaking down the application built in NodeJS MVC.
Here are some of the steps not in details but just an overview:
1. Upload HTML and static contents to a S3 bucket and expose an public url
2. Create REST api's in AWS API gateway that would serve as your controllers to your AWS lambda function that will be accessed from your javascript in your html pages. On access theses API's pass the data and invoke the appropriate AWS Lambda function.
3. The major part is converting yours service and data access layers to lambda functions.
These would be quite challenging but depending on your architecture you can now indeed make a choice.
It is as simple as the figure shown below,
If you have a well built MVC application you can convert your entire application to AWS API gateway - Lambda execution model and make your services deploy in Lambda without the need to maintain an explicit server.
If you want to go more in depth of AWS Lambda here are some links that will give a direction and moreover you can run lambda locally and then deploy on AWS.
1. Get started with AWS Lambda on cloud
2. AWS SDK are available in quite a number of tools
This is just a representation of my experience to leverage API gateway - lambda execution model to have a server-less and easy deployment strategy for micro services. One can always decide which model is the right fit for their application.
MVC or not-MVC is indeed a choice now.
I hope this article provides an overview of how you can consider this model to MVC and change a server deployed application to server-less.
Cheers.
I was given the opportunity to work on it take it further. I was hard stuck that MVC is the best existing model to decouple your project and have easier code management.
Perhaps this discussion changed it all:
Chandi: Hey! you've got to work on dashboardLets begin with understanding a simple MVC application irrespective of any programming language. There are 3 components involved Model-View-Controller.
Me: Sounds good! What's it built on ?
Chandi: Its a MVC Node JS application and there is no sessions management, database etc just an API calls to google analytics and display in charts.
Me: MVC in node JS wow that's nice!
Chandi: No!! MVC is not needed here, have a look at AWS lamda - API gateway model ?
Me: MVC is good! I don't see any point here ?
Chandi: Check it out and you'll know!
<after a while | after reading>Me: Whaaaatt! No server ?
Chandi: Haha
There are quite a number of MVC frameworks out there. Some of them back of mind would be spring MVC in Java, Express in Node.js. When a request arrives to the server it first lands on the front controller as shown in the figure above. In spring MVC its the dispatcher servlet or Node.js its app.js/server.js (the file that declare itself as a server application. There a various controllers/routes registered on to the front controller. Based on the URL path the front controller dispatches the request to the entity specific controller.
So lets take an example https://www.domain.com/app_name/entity_path/entity_api_method
Now as soon as the request arrives to Front Controller it checks for the entity_path registered with it and forwards the request to the entity specific controller. Then in that controller it scans for the API that matches 'entity_api_method' and renders the specific view or returns model for service/data access layer or any 3rd party API can be consumed here. All of this is deployed on a server.
My application did not have a database, no session management, no user access etc. Why do I need a server? Well I only realized when I read that blog by Tim Wagner.
How do I refactor my MVC application to a server-less architecture and avoid the overhead of an explicit server managementNow lets understand AWS API gateway - Lambda execution model.
Amazon provides EC2 or Elastic bean stalk (an environment to configure n instances of EC2) that can help you deploy your web application. However these configurations still host a server or is a server. But we decided a server-less architecture.
Here, AWS Lamda comes to the rescue!
Q: What is AWS Lambda?
"AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay only for the compute time you consume - there is no charge when your code is not running. With Lambda, you can run code for virtually any type of application or backend service - all with zero administration. Just upload your code and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability. You can set up your code to automatically trigger from other AWS services or call it directly from any web or mobile app " - AWS faq.
Lets start breaking down the application built in NodeJS MVC.
Here are some of the steps not in details but just an overview:
1. Upload HTML and static contents to a S3 bucket and expose an public url
2. Create REST api's in AWS API gateway that would serve as your controllers to your AWS lambda function that will be accessed from your javascript in your html pages. On access theses API's pass the data and invoke the appropriate AWS Lambda function.
3. The major part is converting yours service and data access layers to lambda functions.
These would be quite challenging but depending on your architecture you can now indeed make a choice.
It is as simple as the figure shown below,
If you have a well built MVC application you can convert your entire application to AWS API gateway - Lambda execution model and make your services deploy in Lambda without the need to maintain an explicit server.
If you want to go more in depth of AWS Lambda here are some links that will give a direction and moreover you can run lambda locally and then deploy on AWS.
1. Get started with AWS Lambda on cloud
2. AWS SDK are available in quite a number of tools
This is just a representation of my experience to leverage API gateway - lambda execution model to have a server-less and easy deployment strategy for micro services. One can always decide which model is the right fit for their application.
MVC or not-MVC is indeed a choice now.
I hope this article provides an overview of how you can consider this model to MVC and change a server deployed application to server-less.
Cheers.